4C
DIAMONDS ARE EARTH’S GIFT TO WOMEN

4C
DIAMONDS ARE EARTH’S GIFT TO WOMEN
Diamonds were mesmerizing since the beginning of time. Their story evolves along the history of mankind. Since the very first centuries, diamonds have been considered the most precious not of amongst precious stones, but amongst practically anything in the world.
What is really important is for us to realize that each and every diamond is unique. Every gem is a one of the kind combination of shape, colour, weight, internal and external characteristics.
But, what exactly makes diamonds so special? A gemologist will refer to the circumstances it is created, below the surface of the Earth. An economist will value them based on scarcity and stock value. The consumer will focus on the beauty, the charm and the memory that comes with it. In fact, all the above are valid.
Beyond the emotions and awe that every diamond triggers, there is a scientific field that studies and certifies the uniqueness and value of each gem. Gemologists- like Venetia and Stella Vildirides- specialize in the methods determining the weight (in Carats), the clarity of the stone, the colour and cut of each diamond, in order to categorize each stone according to its value.
Our expert's team in all Venetia Vildirides store will consult you on how to select the appropriate diamond for each occasion. However, there you can find some preliminary information on the parameters that determine the value of the gem and the variety of cuts.
COLOUR AND CUT ARE THE MOST SIGNIFICANT CHARACTERISTICS OF A DIAMOND, AS THEY DETERMINE HOW IT LOOKS.
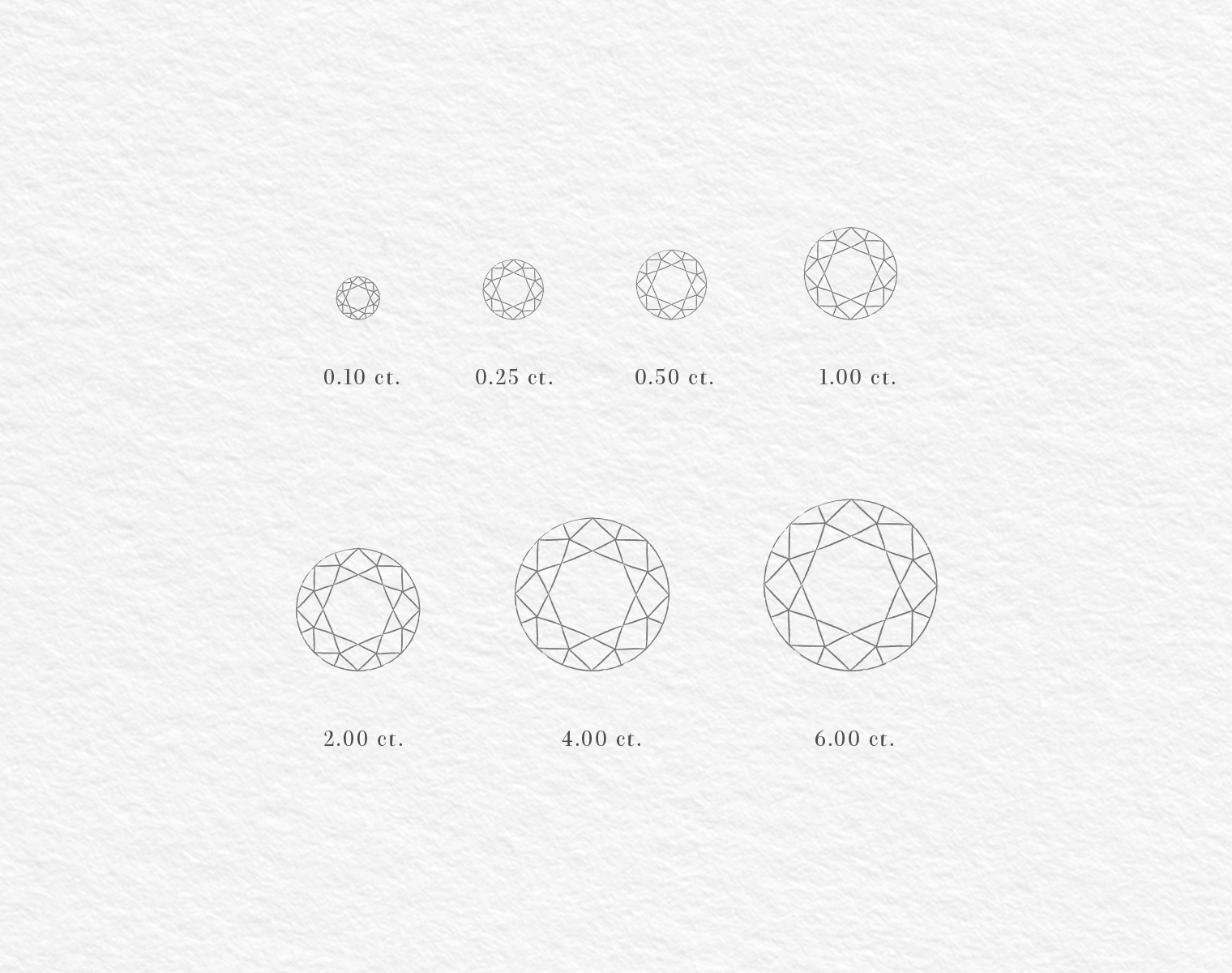
”CARATS
Diamond weight is measured in carats. One carat equals 200mg, thus a diamond weighing one gram is a 5 carats diamond. Two gems of the same carat weight can differ significantly in price, as all four evaluators are equally important. Ceteris paribus, the heavier the diamond the scarcer and therefore more expensive it is.
COLOR
Or, to put it correctly, its absence. The more the colorlessness of the diamond, the purer it’s composition and its value. But, differences in color are subtle and usually very difficult to see. This is why the Gemology Institute of America introduced a new metric system, which is now universally adopted.
GIA’s D-to-Z diamond color-grading system measures the degree of colorlessness by comparing a stone under controlled lighting and precise viewing conditions to masterstones of established color value. Diamonds that are more yellow or brown than category Z or of completely different colours are categorized under “Fancy Color Diamonds”- which are very rare and of very high value. In this class, the more the colour, the higher the value. And, although the difference in the colour scale can be imperceptible, its impact on the diamond’s valuation is disproportionally big.

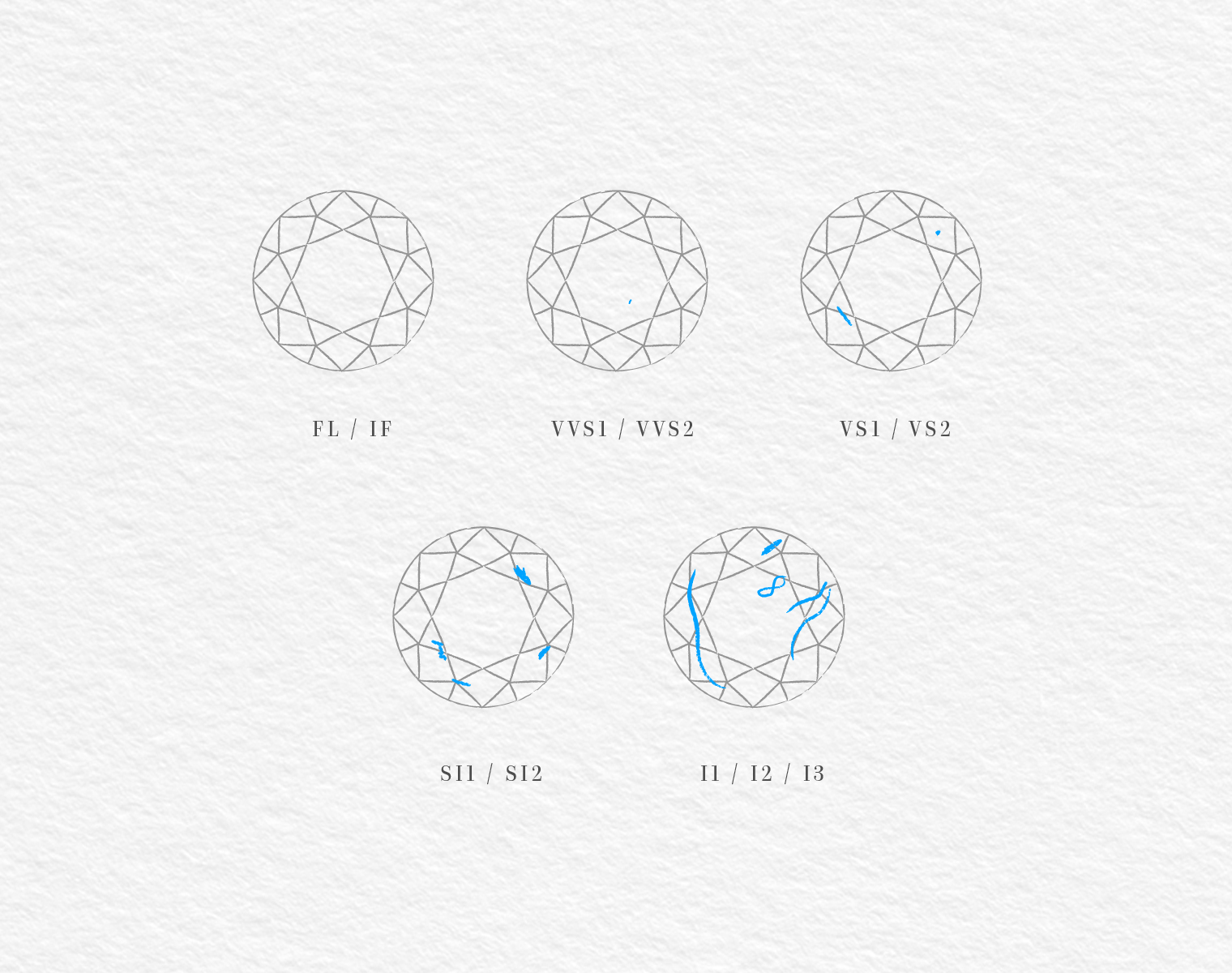
CLARITY
A diamond’s clarity is defined under a microscope in 10x scale. The gemologist is searching for a variety of internal characteristics called “inclusions” and external characteristics called “blemishes” and classifies the diamond according to the size, the type, the amount, the classification and their color.
The G.I.A. Clarity Scale has 11 grades, with the highest ranking to be the Flawless and the lowest being the Inclusive. Flawless diamonds are particularly rare and they are priced accordingly. Diamonds classified in the following categories are equally charming and unique in their own manner: like fingerprints, no two of them are ever the same.
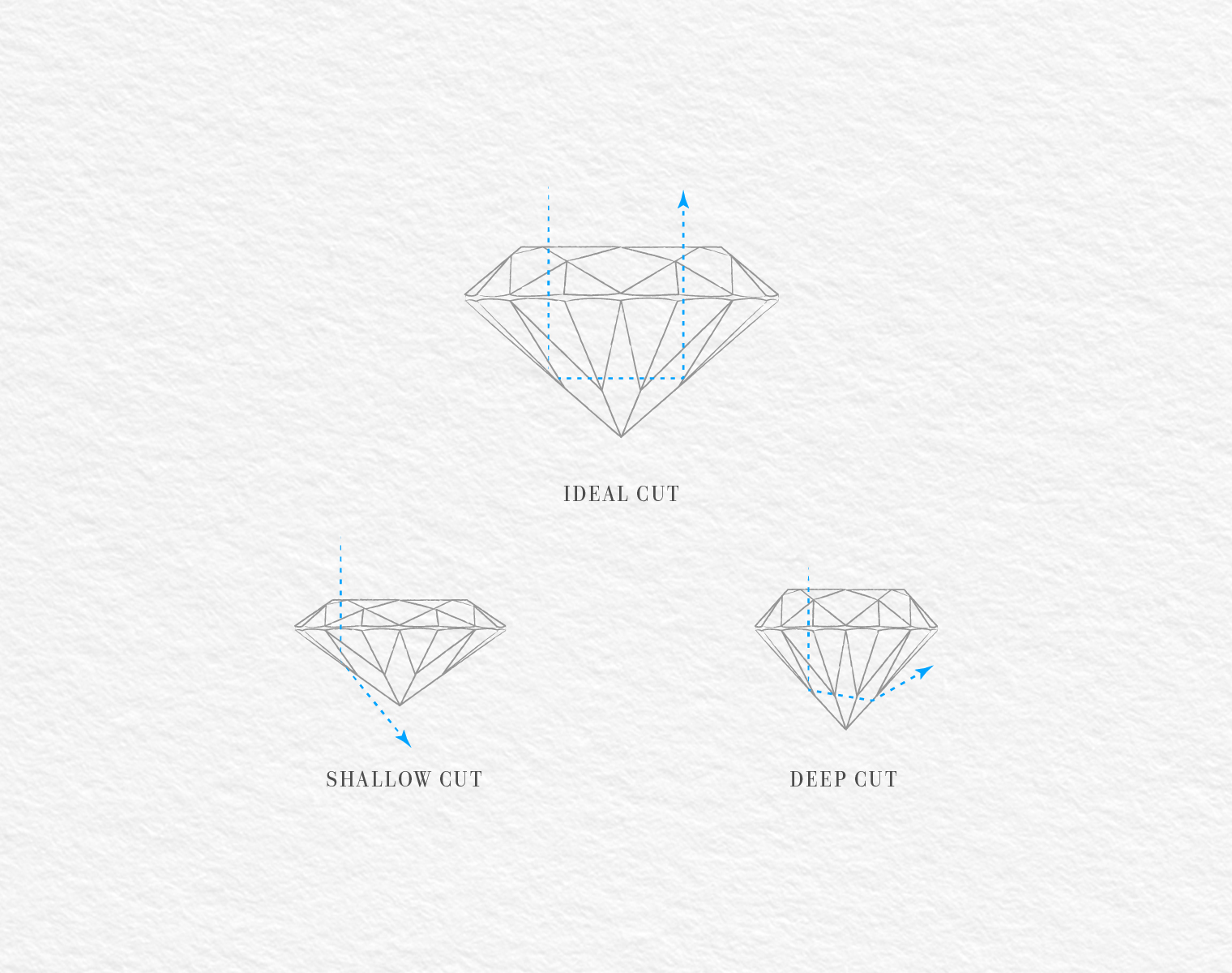
CUT
Diamond Cut is the most significant element of the four as it affects the overall appearance of the stone. However, two different things are described with the word “cut”: The first is the shape of the stone. The second is its proportions, as they determine how the light is diffused, and, consequently, the brightness. Diamonds have the unique quality to create iridescence as the light is reflected, a result that is the resultant of dimensions, analogy, symmetry and polish. The cut of each diamond adds a distinctive shine by allowing the light to touch the surface of the stone and then to be reflected. The perfect diamond cut is neither too deep or too shallow so that the reflections and iridescence are allowed but no shadows are created.
Diamond cut grading scale extends from excellent to poor. Experts assess cut as a whole, the proportions and the polish.
For the assessment of the color, the gemologist uses ultraviolet (UV) light to examine the fluorescence of the gem. This is not a characteristic of every single diamond-in fact only 35% of the gem population has it - and its presence explains perfectly the price difference between two diamond with all the other elements being identical. A stone of bright color with intense fluorescence will look “milky” in natural light, which is not the desirable appearance for a diamond. Nevertheless, a stone placed low in the color grading scale, below J, fluorescence might smooth the yellowish or brownish tones.

